About This Publication
This paper was presented at the 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) and represents research conducted at the University of Tennessee, Knoxville, in the Min-Kao Department of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science.
Authors: Robert Coop and Itamar Arel
Abstract
Catastrophic forgetting (or catastrophic interference) in supervised learning systems is the drastic loss of previously stored information caused by the learning of new information. While substantial work has been published on addressing catastrophic forgetting in memoryless supervised learning systems (e.g. feedforward neural networks), the problem has received limited attention in the context of dynamic systems, particularly recurrent neural networks. In this paper, we introduce a solution for mitigating catastrophic forgetting in RNNs based on enhancing the Fixed Expansion Layer (FEL) neural network which exploits sparse coding of hidden neuron activations. Simulation results on several non-stationary data sets clearly demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed architecture.
Key Contributions
The Problem: Catastrophic Interference
Catastrophic interference is a well-known characteristic of many parametric learning systems where exposure to new information results in severe loss of previously learned information. This extreme loss cannot be attributed to the inherent informational capacity of the learning system, but rather is caused by the overlap of representations within the learning system.
Many real-world applications, such as financial time series analysis and climate prediction, involve data streams that are either strictly non-stationary or can at best be considered piecewise stationary. These problem domains require algorithms that address the stability-plasticity dilemma and find a balance between learning new information and retaining previously learned representations.
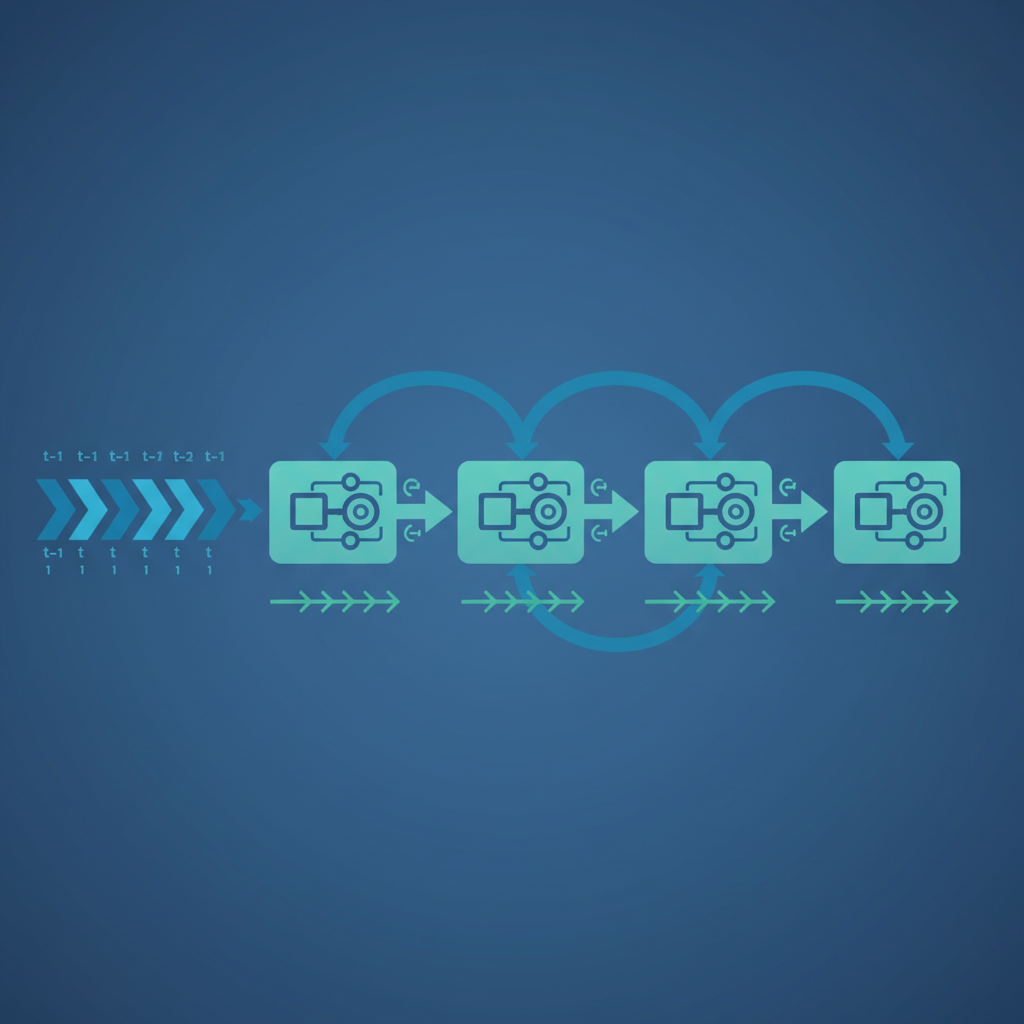
The Solution: Recurrent Fixed Expansion Layer (rFEL) Network
The paper introduces the Recurrent Fixed Expansion Layer (rFEL) network, which extends the FEL architecture to handle temporal sequences. Key aspects include:
-
Sparse Encoding: The FEL neurons protect input-to-hidden layer weights from portions of the backpropagated error signal, preventing network weights from changing drastically when exposed to new information.
-
L1 Norm Minimization: The approach ensures sparsity by minimizing the L1 norm of the fixed expansion layer neurons while retaining key information from the hidden layer neurons, using the feature-sign search algorithm.
-
Context Signal Gating: In the rFEL network, the expansion layer acts to prevent convergence of weights between context neurons and hidden layer neurons by gating the context signal.
Experimental Results
The paper demonstrates the effectiveness of the rFEL network through multiple experiments:
-
Auto-associative Binary Sequence Reconstruction: The rFEL network exhibited pseudo-linear degradation while other schemes (pseudorehearsal, activation sharpening, dual networks) followed sharper degradation profiles.
-
Non-stationary MNIST Sequence Classification: Under non-stationary conditions, the rFEL network significantly outperformed other algorithms, maintaining accuracy even when other methods experienced rapid performance drops.
Significance
This research addresses a fundamental challenge in neural network design that remains relevant today. The ability to learn continuously without forgetting previously acquired knowledge is crucial for:
- Lifelong learning systems
- Online learning applications
- Adaptive systems operating in non-stationary environments
- Real-world AI applications requiring incremental learning
The sparse coding approach presented in this paper laid groundwork for subsequent research in continual learning and has influenced modern approaches to preventing catastrophic forgetting in deep learning systems.
Download
Citation
@inproceedings{coop2013mitigation,
title={Mitigation of Catastrophic Forgetting in Recurrent Neural Networks using a Fixed Expansion Layer},
author={Coop, Robert and Arel, Itamar},
booktitle={2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN)},
year={2013},
organization={IEEE}
}
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA) via Army Research Office (ARO) agreement number W911NF-12-1-0017, and by NSF grant #CCF-1218492.